WCDMA (Wideband Code Division Multiple Access) is a cellular network technology that is part of the 3G (Third Generation) wireless communication standard. It provides high-speed data and voice services to mobile devices. Here’s a pointwise description of WCDMA technology:
- 3G Standard: WCDMA is one of the key technologies used in the 3G standard, offering improved data rates and capacity compared to its predecessor, 2G (GSM) networks.
- Wideband Code Division Multiple Access: WCDMA uses a wideband spread spectrum technique known as CDMA to allow multiple users to share the same frequency band simultaneously. It employs a wider bandwidth than traditional CDMA to achieve higher data rates.
- Frequency Bands: WCDMA operates in various frequency bands, including 850 MHz, 900 MHz, 1700/2100 MHz, and 1900 MHz, depending on the region and network operator.
- Radio Access Network (RAN): WCDMA networks consist of a Radio Access Network that includes Base Transceiver Stations (BTSs), Node-Bs, and Radio Network Controllers (RNCs). The RAN handles the wireless communication between mobile devices and the core network.
- Node-B: The Node-B is the WCDMA equivalent of the GSM Base Transceiver Station (BTS). It comprises transceivers, antennas, and associated equipment responsible for transmitting and receiving signals within a specific coverage area, known as a cell.
- Coverage Area: Each Node-B has a specific coverage area, with cell sizes varying depending on factors such as transmit power, antenna configuration, and environmental conditions.
- Spreading Codes: WCDMA utilizes unique spreading codes to differentiate between users and allow simultaneous transmission and reception of multiple signals on the same frequency band.
- Channelization: WCDMA divides the available bandwidth into multiple channels, each assigned to a specific user or communication session. These channels include dedicated channels for voice, data, and control information.
- High Data Rates: WCDMA provides high-speed data transmission, offering theoretical maximum downlink speeds of up to 14.4 Mbps (megabits per second) and uplink speeds of up to 5.76 Mbps, depending on network configuration and device capabilities.
- Voice and Data Integration: WCDMA supports simultaneous voice and data transmission, allowing users to make calls while accessing data services such as internet browsing, email, and multimedia streaming.
- Soft Handover: WCDMA networks employ soft handover techniques, enabling seamless handovers as mobile devices move between cells. Soft handover ensures uninterrupted call quality and enhances coverage and network reliability.
- Power Control: WCDMA employs power control mechanisms to optimize the transmission power of mobile devices. This helps conserve battery life, reduce interference, and maintain signal quality.
- Radio Network Controller (RNC): The RNC is responsible for managing and controlling multiple Node-Bs within a WCDMA network. It handles tasks such as call setup, handover management, radio resource allocation, and network optimization.
- Signaling and Control: WCDMA uses various protocols and procedures for signaling and control between mobile devices, Node-Bs, and the core network. These include call setup, call termination, mobility management, and quality of service control.
- Network Optimization: WCDMA networks undergo continuous optimization to improve performance and capacity. Techniques such as power control, handover optimization, load balancing, and interference mitigation are employed to enhance network efficiency.
- Security: WCDMA incorporates security measures to protect voice and data communications. Encryption algorithms, authentication protocols, and privacy mechanisms ensure the confidentiality and integrity of user information.
- Interoperability: WCDMA adheres to international standards set by organizations like the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), ensuring interoperability between network equipment from different vendors and seamless roaming for mobile subscribers.
- Evolution to 4G and Beyond: WCDMA serves as a foundation for subsequent generations of wireless technology, such as 4G (LTE) and 5G (NR). Network operators can upgrade their existing WCDMA infrastructure to support higher data rates, improved latency, and advanced features.
- User Equipment (UE): WCDMA-compatible mobile devices, known as User Equipment (UE), include smartphones, tablets, and other wireless devices that can access WCDMA networks. These devices require WCDMA-capable chipsets and modems to connect to the network.
- Future Developments: Ongoing research and development focus on further enhancing WCDMA technology. Areas of interest include energy efficiency, network densification, virtualization, and the integration of advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
In summary, WCDMA technology plays a crucial role in 3G wireless networks, offering high-speed data transmission, voice services, and seamless connectivity. With its wideband CDMA approach, soft handover capabilities, and advanced network optimization techniques, WCDMA has enabled significant advancements in mobile communications.
Some more information
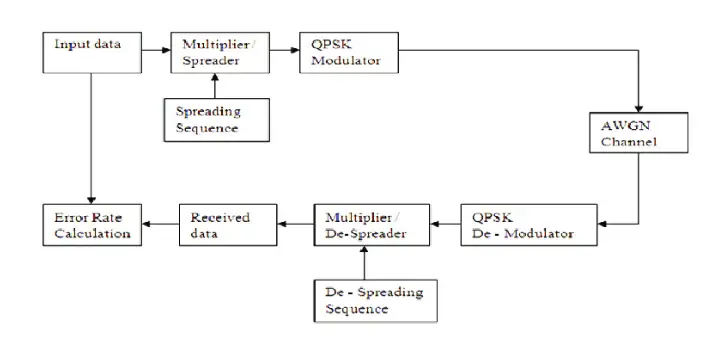
WCDMA system block diagram
The following are the key components of a WCDMA system:
- User Equipment (UE): The UE is the mobile device, such as a smartphone or tablet, that communicates with the WCDMA network.
- Base Station (BS): The BS is the fixed infrastructure that communicates with the UEs.
- Node B: The Node B is a physical unit that is part of the BS. It is responsible for radio transmission and reception, as well as data processing.
- Radio Network Controller (RNC): The RNC is a central unit that manages the radio resources in the network. It is responsible for routing calls between UEs, as well as for providing services such as call forwarding and voicemail.
- Home Location Register (HLR): The HLR is a database that stores information about UEs, such as their subscriber identity, phone number, and billing information.
- Visitor Location Register (VLR): The VLR is a database that stores information about UEs that are currently roaming in the network.
WCDMA uses a variety of technologies to transmit voice and data, including:
- Spread spectrum modulation: Spread spectrum modulation is a technique that spreads the data signal over a wider frequency range. This makes the signal less susceptible to interference and allows multiple users to share the same radio frequency band.
- Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM): OFDM is a technique that divides the data signal into a number of smaller, orthogonal subcarriers. This allows the data signal to be transmitted more efficiently and with less interference.
- Forward error correction (FEC): FEC is a technique that adds redundancy to the data signal. This allows the receiver to correct errors that occur during transmission.
WCDMA is a complex technology, but it offers a number of advantages over previous cellular network technologies, including:
- High capacity: WCDMA can support more users per cell than previous cellular network technologies.
- Robustness: WCDMA is robust and can operate in a variety of environments, including in areas with high levels of interference.
- Efficiency: WCDMA is efficient in terms of power consumption and spectrum usage.
- Scalability: WCDMA is scalable, and can be easily expanded to meet growing demand.
WCDMA is a mature and reliable technology that has been deployed in over 190 countries and territories. It is the most widely used 3G cellular network standard in the world, and it is expected to continue to be used for many years to come.


