Skip to content
- ntroduction of ENIAC:
- The Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer (ENIAC) stands as a milestone in computing history, marking the advent of electronic digital computers.
- Developed during the 1940s, amidst World War II, ENIAC represented a leap forward in computational capabilities, offering unprecedented speed and versatility compared to previous mechanical and electromechanical machines.
- Massive Scale:
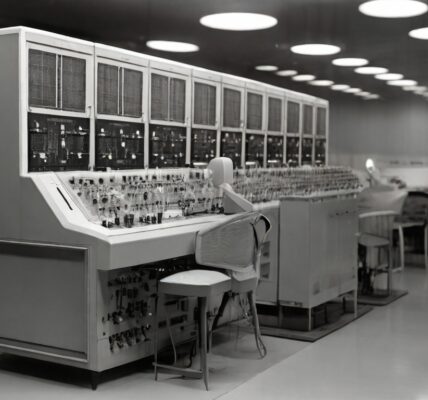
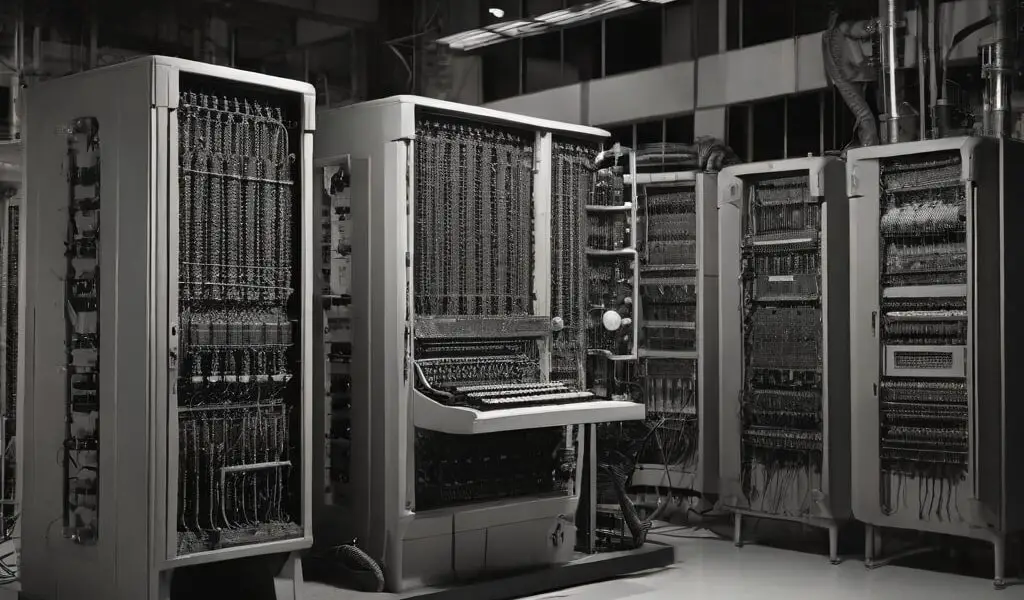
- ENIAC was a behemoth of a machine, occupying a significant amount of space within its dedicated room at the University of Pennsylvania’s Moore School of Electrical Engineering.
- Comprising thousands of vacuum tubes, resistors, capacitors, and other electronic components, ENIAC’s sheer size and complexity were a testament to the early challenges of electronic computing.
- Vacuum Tube Technology:
- Central to ENIAC’s operation were vacuum tubes, electronic devices used to amplify and switch electrical signals.
- Vacuum tubes served as the primary means of processing and storing data in ENIAC, allowing for rapid calculations through the manipulation of electronic signals.
- However, vacuum tubes were not without drawbacks, as they were prone to overheating, consuming significant power, and requiring frequent maintenance.
- Versatility in Calculations:
- ENIAC was designed to perform a wide range of numerical computations, including ballistic trajectory calculations vital for wartime artillery targeting.
- Its programmable nature enabled engineers to reconfigure the machine for various tasks by manually rewiring its connections, a time-consuming process that limited its flexibility compared to modern programmable computers.
- Pioneering Programmers:
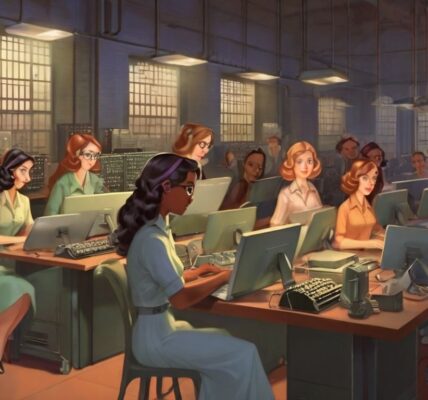
- ENIAC’s operation relied on a team of skilled mathematicians and engineers who programmed the machine by physically setting switches and adjusting cables to define the desired computational tasks.
- Notably, six female mathematicians, often referred to as the “ENIAC Programmers,” played a crucial role in programming and operating ENIAC, highlighting the significant contributions of women to early computing.
- Impact and Legacy:
- ENIAC’s successful operation demonstrated the potential of electronic digital computers to revolutionize computation, paving the way for further advancements in computing technology.
- Its influence extended beyond military applications, influencing the development of subsequent generations of computers and inspiring future generations of computer scientists and engineers.
- Technological Evolution:
- While ENIAC represented a groundbreaking achievement in its time, subsequent developments in computing technology, such as the invention of the transistor and the integrated circuit, would lead to smaller, faster, and more reliable computers.
- The principles pioneered by ENIAC laid the foundation for the modern digital era, shaping the evolution of computing from room-sized machines to handheld devices that are integral to everyday life.
- Conclusion:
- ENIAC’s development marked a pivotal moment in the history of computing, showcasing the potential of electronic digital computers to solve complex mathematical problems and process vast amounts of data.
- Despite its limitations, ENIAC’s legacy endures as a testament to human ingenuity and innovation, serving as a symbol of the relentless pursuit of progress in the field of computing.